Progressive Web Apps vs Native Apps: Which to Choose in 2026
Explore the key differences between Progressive Web Apps and Native Apps, including performance, cost, user experience, and offline capabilities. This guide helps businesses decide which app type best fits their goals, audience, and development strategy.

Businesses today must carefully evaluate digital strategies before deciding between Progressive Web Apps and Native Apps. Both options offer unique advantages in performance, accessibility, development costs, and long-term scalability.
Understanding the differences between progressive web apps vs native solutions helps organizations align technology choices with their strategic goals. This guide explores the features, benefits, and limitations of progressive web apps vs native apps. Let’s dive in.
Key Takeaways
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer cross-platform compatibility with lower development and maintenance costs.
- Native Apps deliver superior performance, full hardware access, and advanced offline capabilities.
- PWAs are ideal for content-focused apps, marketing campaigns, and rapid deployment.
- Native Apps are best for complex, graphics-heavy, or performance-intensive applications.
- Budget, timeline, audience, and functionality should guide the choice between PWAs and Native Apps.
What Are Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)?
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are web applications built with standard technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They function across multiple devices and browsers, delivering fast, reliable, app-like experiences.
PWAs can be added to a device’s home screen, load instantly, and adapt smoothly to different screen sizes for a native-style feel. Using service workers and a web app manifest, PWAs enable offline access, push notifications, and background syncing for uninterrupted usability.
This makes PWAs an efficient solution for businesses seeking both reach and performance.
What Are Native Apps?
Native apps are software programs built specifically for a particular mobile operating system, such as iOS or Android. Developers write native apps using platform-specific languages and tools, such as Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android.
These apps are downloaded and installed directly from app stores, giving users seamless access and trust through official distribution channels. Native apps can fully leverage a device’s hardware features, such as cameras, sensors, and GPS, to deliver high performance.
Because they integrate tightly with the operating system, native apps often deliver faster performance and a smoother experience than browser-based alternatives.
Progressive Web Apps vs Native Apps: Key Differences
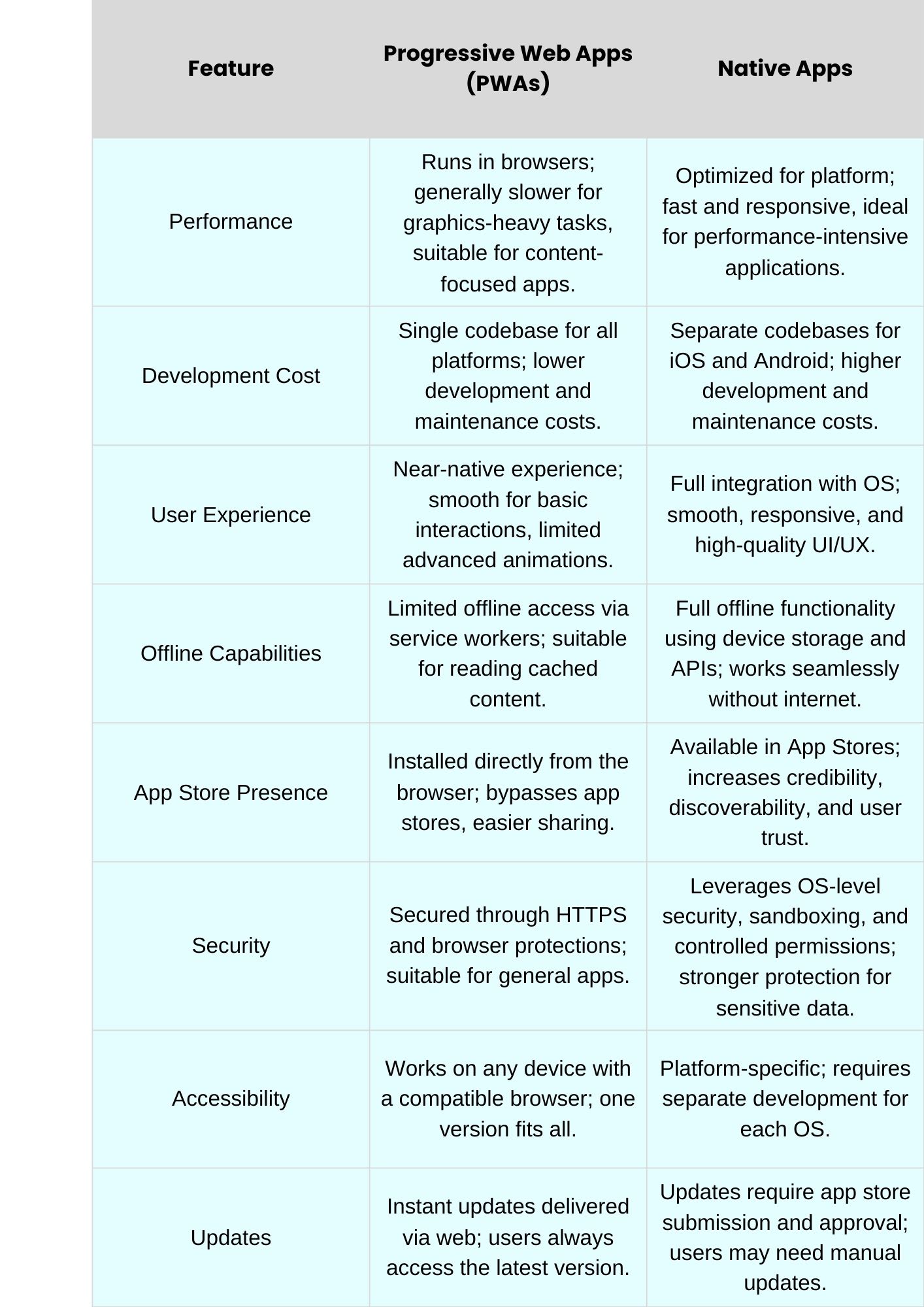
Understanding the key differences between progressive web apps vs native apps helps businesses choose the right solution. Here are the key differences:
1. Performance
Native apps deliver faster performance because they are built specifically for each platform and optimized for that platform. PWAs rely on browsers, which can create minor delays during complex tasks. Graphics-heavy apps benefit most from native development, while PWAs are ideal for simpler, content-driven applications that prioritize accessibility over raw speed.
2. Development Cost
PWAs use a single codebase across all platforms, significantly reducing development and maintenance costs. Native apps require separate codebases for iOS and Android, increasing costs and timelines, making them more expensive for businesses with tight budgets.
3. User Experience
Native apps integrate deeply with device operating systems, providing smooth animations, full hardware access, and responsive interactions. PWAs offer near-native experiences but may fall short in performance-intensive operations or advanced UI effects.
4. Offline Capabilities
Native apps function fully offline, leveraging device storage and APIs. PWAs use service workers to cache content, providing limited offline access that is sufficient for reading previously loaded information but not for complex offline operations.
5. App Store Presence
Native apps are published in official app stores, boosting credibility, discovery, and trust. PWAs bypass stores, allowing installation directly from the browser, which improves accessibility but limits organic discovery through app marketplaces.
6. Security
Native apps benefit from OS-level security features such as sandboxing and granular permissions, providing stronger protection. PWAs rely on HTTPS and browser security, offering safe but slightly limited protection for sensitive or transactional data.
Advantages of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
- Lower development & maintenance cost: PWAs use a single codebase, significantly reducing both development and long-term maintenance expenses.
- Cross-platform compatibility with one codebase: PWAs run on multiple devices and browsers, eliminating the need for separate platform development.
- SEO & web discoverability: PWAs are indexed by search engines, improving visibility and organic traffic potential for businesses.
- Quick deployment & instant updates: Updates are delivered instantly via the web, ensuring users always have access to the latest version.
- Less storage space on user devices: PWAs use minimal device storage, enabling quick, accessible installation for users with limited space.
Disadvantages of Progressive Web Apps
- Limited access to device hardware features: PWAs cannot fully utilize cameras, AR, sensors, or other advanced device functionalities.
- Not always available in app stores (visibility issues): PWAs bypass app stores, reducing discoverability and perceived credibility.
- Performance limitations for complex, graphics-heavy apps: PWAs may lag under heavy workloads or multimedia-intensive applications compared to native apps.
- Some platform/browser restrictions (iOS especially): Certain features may not work consistently across all devices or operating systems.
Advantages of Native Apps
- Maximum performance & speed: Native apps are fully optimized for specific platforms, providing smooth, responsive, and high-performance experiences.
- Full access to all device hardware features: Native apps can leverage GPS, cameras, sensors, and other hardware for advanced functionality.
- Better offline capabilities: Native apps can operate fully offline, storing data and providing full access without an internet connection.
- App store presence boosts trust & discovery: Publishing on official app stores increases credibility, user trust, and discoverability among target audiences.
- Advanced engagement features (push notifications, analytics): Native apps support push notifications and analytics tracking, enabling deep user engagement for marketing and retention.
Disadvantages of Native Apps
- Higher development & maintenance cost: Separate codebases for iOS and Android increase both initial development and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Longer development & release cycles (app store reviews): App store reviews require approval, which can slow feature delivery and bug fixes.
- Requires separate codebases for different platforms: Native development demands platform-specific programming, making simultaneous multi-platform releases more challenging.
- More storage is used on devices: native apps consume significant storage, which may discourage installation on space-limited devices.
When to Choose Progressive Web Apps vs Native Apps
Businesses should consider Progressive Web Apps when aiming to reach a broad audience across multiple platforms. PWAs are ideal for content-focused applications, marketing campaigns, or minimum viable products that require rapid deployment and low development cost.
Native apps are better suited for performance-intensive applications that require full access to device hardware, advanced user interactions, and offline capabilities. Organizations that prioritize seamless user experiences, gaming, AR features, or heavy multimedia content will benefit most from native app development.
Budget, timeline, target audience, and required functionalities should guide the choice between progressive web apps and native solutions. Companies seeking rapid updates and cross-platform accessibility may prefer PWAs, whereas those demanding high performance and feature-rich apps should opt for native development.
How to Choose: PWA vs Native
Choosing between a Progressive Web App and a native app depends primarily on your business goals and resources. PWAs are ideal for companies aiming to reach a broad audience quickly while minimizing development and maintenance costs. They work best for content-driven platforms, marketing campaigns, or minimum viable products requiring rapid deployment across multiple devices.
Native apps are better suited to applications that require high performance, full access to device hardware, and advanced offline capabilities. They excel in gaming, AR, multimedia, or enterprise solutions where seamless user experience and responsiveness are critical.
Ultimately, factors such as budget, timeline, target audience, required functionality, and long-term scalability should guide the decision between progressive web apps vs native apps. Organizations prioritizing accessibility and fast updates may prefer PWAs, whereas those requiring maximum performance and advanced features should invest in native development.
Build the Perfect App for Your Business Goals
If your business needs expert support choosing between progressive web apps vs native apps, WorkersLab’s mobile app development services deliver high‑performance solutions tailored to your goals. We build intuitive, App Store‑ready native applications with optimized performance, clean code, and seamless user experiences.
Whether you want cross‑platform reach or advanced native features, our team ensures quality from design to launch. Contact us now to start building an app that truly works.
FAQs
Can Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) work offline like native apps?
PWAs can function offline using cached content managed by service workers, which enables access to previously loaded pages and basic interactions. However, their offline capabilities are more limited than native apps, which typically can operate without an internet connection.
Do users need to download a PWA from an app store?
No. PWAs are accessed directly through a web browser and can be installed on the home screen without visiting an app store. This reduces download friction and improves accessibility compared to traditional app installations.
Which is cheaper to develop: a PWA or a native app?
In most cases, PWAs are more cost‑effective because they use a single codebase across platforms. Native apps require separate development for iOS and Android, increasing both development and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Conclusion
Choosing between Progressive Web Apps and Native Apps depends on your business goals, budget, and required functionality. PWAs offer broad accessibility, lower development costs, and quick updates, while native apps provide superior performance, full hardware access, and advanced features. Evaluate your audience, app complexity, and long-term strategy to select the solution that delivers the best user experience and business impact.